Tailor-Made Business Services in Ukraine
Whether you intend to start a stand-alone business or a subsidiary of your existing business it will be important to have an ally on the ground in Ukraine with extensive knowledge of, and experience navigating, the local business landscape.

Western Management
The Leinonen Ukraine office has Finnish management on-site who take a familiar western approach to providing services. An approach based on transparency and accountability.
12
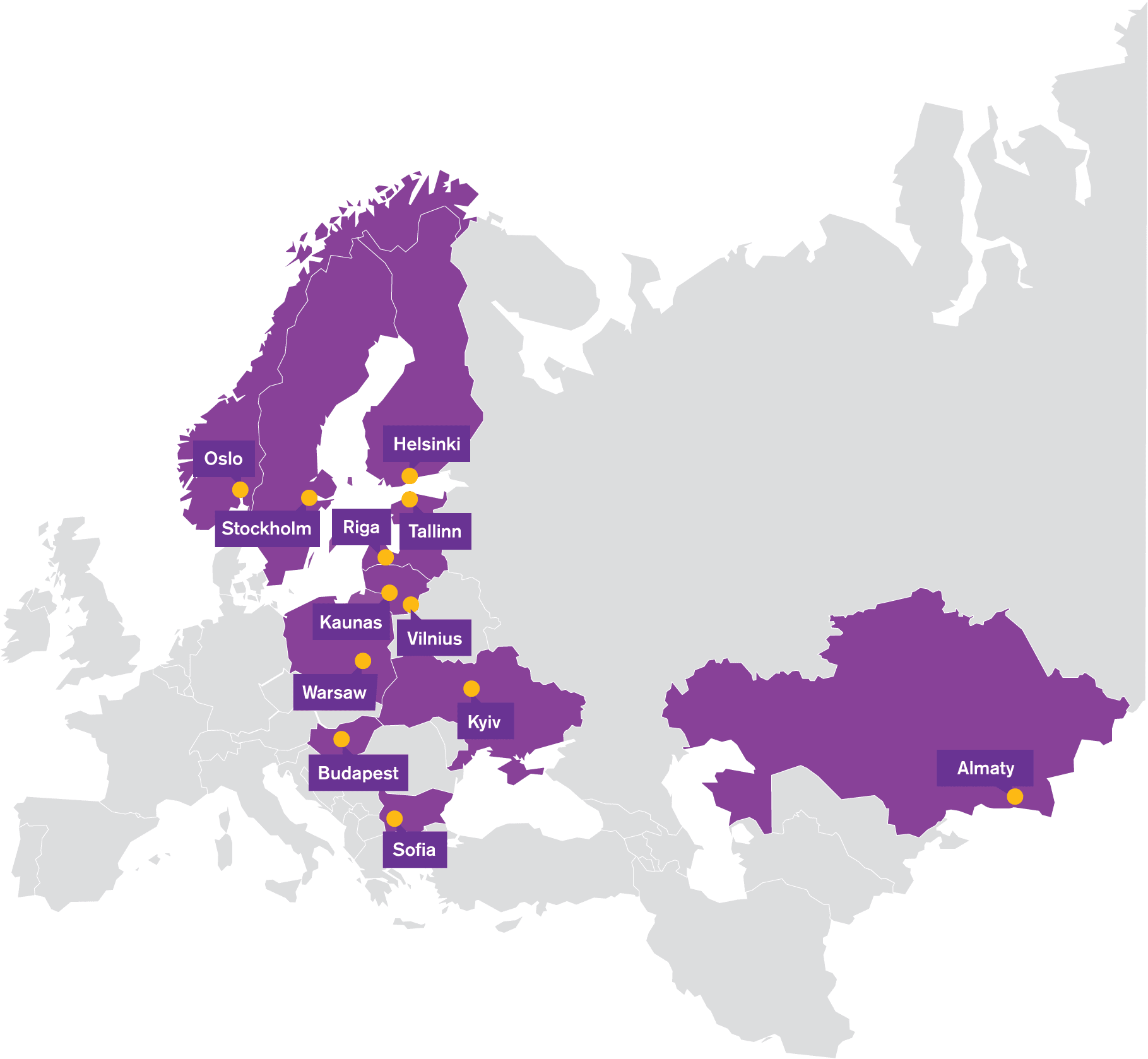
Offices
that we have
34
Years
in business
1500+
Satisfied
customers
11
Countries
we operate in
About Leinonen



Leinonen has been operating for more than 34 years in the business. We have hundreds of professional financial specialists with multilingual skills. We work extensively cross-border and we have more than 1500 long-term clients.
We are proud to offer a high-quality, tailor made service with outstanding communication and reliability. When you work with Leinonen, you will feel that you have a stable, long-term partner supporting you in Ukraine.

The Benefits of Working with Leinonen, Ukraine
Safety of funds
When setting up a business in an unfamiliar environment it is always a good idea to entrust a reliable third party with oversight of your funds. Leinonen can act as that trusted third party.
Future predictability
Accurate financial information will enable you to better identify financial or market trends. This, in turn, will help ensure you are not caught off guard by shifting market dynamics.
Local knowledge
When setting up a business you don’t necessarily have time to keep up with developments that could affect your company. The team at Leinonen always have their ear to the ground.
Services
Reassure your expanding operations will be manageable and profitable



Our network of highly trained and experienced accountants and lawyers in different countries will support your company on an ongoing basis while minimizing your cost.
We have a dead-easy 3-step process for when you take off
To learn more or to set up a virtual meeting with our Leinonen, Ukraine team fill out the contact form on our website. A member of our staff will get back to you promptly.
Recent Posts
Contact Us
Use the form to send a quick inquiry.